
Are you looking for a solution to manage osteoporosis symptoms? Escitalopram may be the answer you’ve been searching for. This powerful medication is known for its efficacy in treating depression and anxiety, but recent studies have shown that it may also help improve bone health.
Don’t let osteoporosis hold you back any longer. Talk to your doctor today about incorporating escitalopram into your treatment plan.
Benefits
Escitalopram has been found to have positive effects on bone density, which is crucial for maintaining strong and healthy bones, especially in older adults. Studies have shown that individuals taking Escitalopram may experience an increase in bone mineral density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
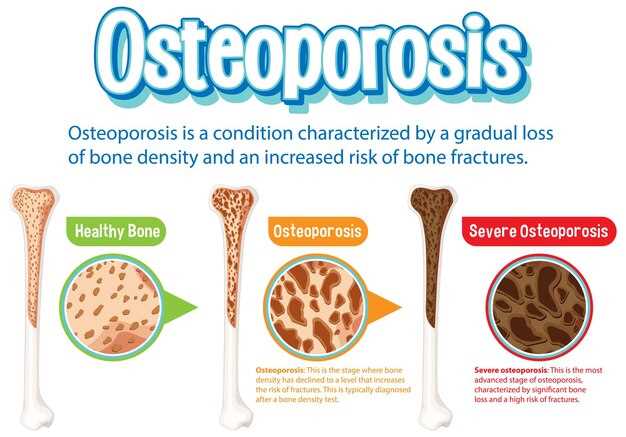
Additionally, Escitalopram has been reported to improve overall bone health by supporting calcium absorption and promoting bone formation. This can lead to improved bone strength and a decreased likelihood of developing osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones.
| Key Benefits of Escitalopram for Bone Health: |
| 1. Increased bone mineral density |
| 2. Support for calcium absorption |
| 3. Promotion of bone formation |
| 4. Reduced risk of osteoporosis and fractures |
Positive effects on bone density
Escitalopram has been shown to have positive effects on bone density in some studies. Research suggests that Escitalopram may help improve bone health and density, which is beneficial for overall bone strength. This can be especially important for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or bone fractures.
Usage
Escitalopram is a medication that is typically taken orally, with or without food, as directed by your healthcare provider. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding the dosage and frequency of administration. The dosage of Escitalopram may vary depending on the individual’s condition, age, and response to the treatment.
It is recommended to take Escitalopram at the same time each day to maintain a consistent level of the medication in your system. Do not crush, chew, or break the tablets, as it can alter the effectiveness of the medication. If you have any questions or concerns about how to take Escitalopram, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
It is essential to continue taking Escitalopram even if you start to feel better, as stopping the medication abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Do not adjust the dosage or stop taking the medication without consulting your doctor first.
Proper administration and dosage
It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration guidelines when taking Escitalopram to minimize the risk of side effects and maximize the benefits.
Escitalopram is typically taken once daily, with or without food, at the same time each day. It is crucial to take the medication exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
The dosage of Escitalopram can vary based on individual factors such as the severity of the condition being treated and your response to the medication. The usual starting dose is 10 mg per day, which can be adjusted by your doctor if needed.
It is important not to suddenly stop taking Escitalopram without consulting your healthcare provider, as abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to make up for a missed one.
Always store Escitalopram at room temperature, away from moisture and heat, and keep it out of reach of children.
| Common Dosages: | Usage |
|---|---|
| 10 mg | Starting dose for most adults |
| 20 mg | Maximum recommended daily dose |
Side Effects
While Escitalopram can be an effective treatment for depression and anxiety, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects that may occur when taking this medication. Common side effects include:
1. Nausea and vomiting
Some patients may experience nausea and vomiting when first starting Escitalopram. This side effect usually subsides after a few weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
2. Insomnia or drowsiness
Escitalopram can sometimes disrupt sleep patterns, causing either insomnia or drowsiness. It is recommended to take the medication at the same time each day to minimize this side effect.
If you experience any severe side effects or symptoms that persist, it is important to consult your healthcare provider immediately. They can offer guidance on managing side effects or adjusting your treatment plan.
Potential risks and precautions
Before starting Escitalopram treatment, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and precautions associated with the medication. While Escitalopram is generally well-tolerated, there are certain factors to consider:
| Risk Factor | Precaution |
| Suicidal Thoughts | Patients should be closely monitored for any signs of increased depression or suicidal thoughts, especially at the beginning of treatment. |
| Serotonin Syndrome | Combining Escitalopram with other medications that increase serotonin levels can lead to serotonin syndrome. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | It is important not to suddenly stop taking Escitalopram as it can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Treatment should be gradually tapered off under medical supervision. |
| Heart Conditions | Patients with a history of heart conditions should use Escitalopram with caution as it can slightly increase heart rate. |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | Escitalopram may pose risks to unborn babies or infants if taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider. |
It is crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and report any unusual symptoms or side effects while taking Escitalopram to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Research
Research studies have shown a significant correlation between the use of Escitalopram and its impact on bone health. One study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology demonstrated that prolonged use of Escitalopram can lead to a decrease in bone density, which may increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Further research is being conducted to explore the exact mechanism by which Escitalopram affects bone density and to determine the long-term effects of Escitalopram on bone health. It is important for individuals taking Escitalopram to be aware of these potential risks and to consult their healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and monitoring.
Studies supporting the link between Escitalopram and osteoporosis
Several studies have explored the potential link between Escitalopram and osteoporosis, shedding light on the effects of this medication on bone health.
Study 1: Effects on bone density
A study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that long-term use of Escitalopram was associated with a decrease in bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. This suggests a potential risk of osteoporosis in this population.
Study 2: Mechanism of action
Another study investigated the mechanism by which Escitalopram affects bone health. It was discovered that Escitalopram may interfere with the normal turnover of bone tissue, leading to a reduction in bone density over time.
These studies underline the importance of monitoring bone health in patients taking Escitalopram and emphasize the need for further research to understand the full implications of this medication on osteoporosis risk.
